Guides
Usage, CMD Options & Troubleshooting
Follow these steps to check status, apply settings, enable protection, and automate Windows Update control using WUB.
Step-by-Step Usage Guide
To manage Windows Update with WUB, check the status indicator, choose Enable or Disable, click Apply, and use Protect Service Settings to keep your selection. This workflow provides predictable service control and clear verification. Reboot if the status does not refresh immediately.
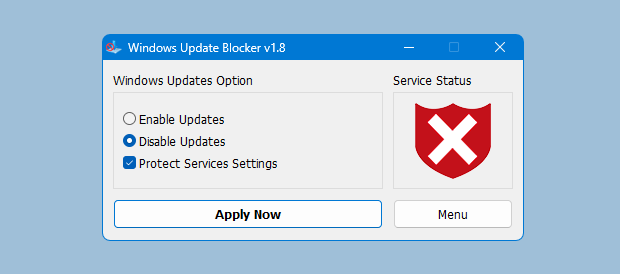
1. Check Status
Open WUB and review the status indicator. Green means updates are enabled; red means they are blocked.
2. Apply Settings
Choose Disable or Enable and click Apply. WUB updates the Windows Update service configuration instantly.
3. Protect Service Settings
Enable the protection option to prevent Windows from re-enabling update services without your consent.
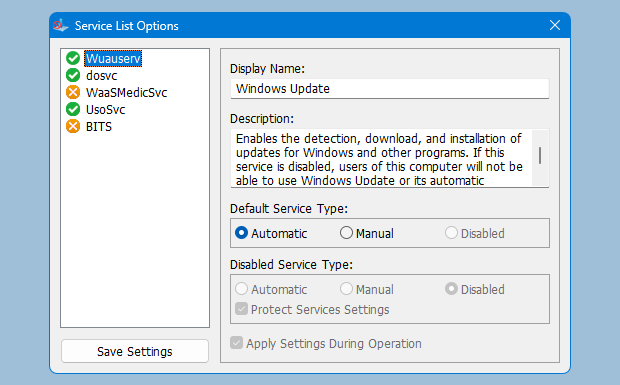
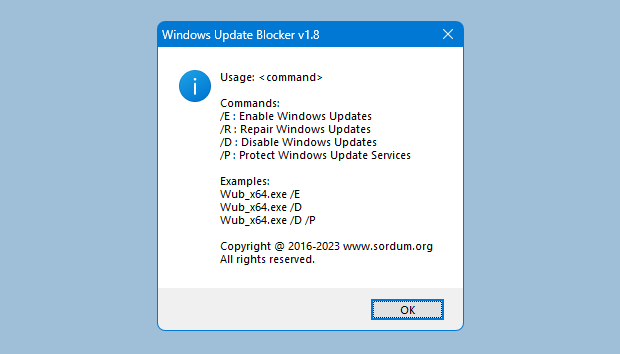
Command Line Arguments
Use Wub.exe with parameters for scripting and automation. Run the command prompt as Administrator for service changes.
- /D — Disable Windows Update services.
- /E — Enable Windows Update services.
- /S — Apply service protection settings.
Reference the WUB command line screen for additional options and status output.
Service Commands (Reference)
WUB automates service control for Windows Update. These commands illustrate the types of service changes typically applied.
sc stop wuauserv
sc config wuauserv start= disabled
sc stop bits
sc config bits start= disabled
sc stop dosvc
sc config dosvc start= disabled
sc stop WaaSMedicSvc
sc config WaaSMedicSvc start= disabledAntivirus Exclusions
If your antivirus blocks WUB, add the Wub.exe location to your allow-list after verifying the file integrity. This prevents false positives caused by service-level changes.
Keep the tool in a dedicated folder so exclusions are easy to manage and audit.
Troubleshooting Access Errors
- Run WUB as Administrator to modify services.
- Disable conflicting policy settings if a managed device blocks changes.
- Reboot after changing service states if the UI status does not refresh.
If errors persist, review Windows Event Viewer logs to identify policy enforcement or service dependency issues.





